Load Balancer Support
Ufo can automatically create a load balancer and associate it with an ECS service. The options:
- Create an ELB.
- Use existing ELB by providing a target group arn.
- Do not create an ELB.
Examples
Here are examples of each of them:
# Create an ELB
ufo ship demo-web --elb=true
# Use existing target group from pre-created ELB
ufo ship demo-web --elb=arn:aws:elasticloadbalancing:us-east-1:123456789:targetgroup/target-name/2378947392743
# Disable creating ELB
ufo ship demo-web --elb=false
Web Service Convention
By convention, if the container name is ‘web’ in the task definition. Deployments of new services will automatically create a load balancer. So if the task definition looks something like the following then a load balancer will automatically be created:
{
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "web",
...
The behavior can be disabled with --elb=false for web containers.
ufo ship demo-web --elb=false
For non-web container the --elb option must be explicitly set to --elb=true if you want a load balancer to be created.
ELB Retained
Ufo retains the ELB setting. So future ufo ship commands will not suddenly remove the load balancer. If you need to change the elb setting, then you need to explicitly set a new --elb value.
Important: Adding and removing load balancers will change the ELB DNS. Please take pre-caution using the elb options. This risk is mitigated if you have configured Route53 support.
ELB Types: Application and Network
Ufo supports application and network load balancer types. To specify the type use --elb-type. Examples:
ufo ship demo-web --elb-type network
ufo ship demo-web --elb-type application # default
ELB Static IP addresses for Network Load Balancers
Network load balancers support static EIP address. You can create a network load balancer using pre-allocated EIP addresses with the the --elb-eip-ids option. Example:
ufo deploy demo-web --elb-eip-ids eipalloc-a8de9ca1 eipalloc-a8de9ca2
If you use the --elb-eip-ids option, ufo assumes you want an --elb-type=network since only network load balancers support EIPs.
When specifying the --elb-eip-ids option, the list length must be the same as the number of subnets configured in your .ufo/settings/network/default.yml profile. The --elb-eip-ids setting is optional. If you do not specify it, a network load balancer will still be created.
If you need to change the EIPs for existing services, you might get a “TargetGroup cannot be associated with more than one load balancer” error. To work around this you can set the env variable UFO_FORCE_TARGET_GROUP=1 which will force a re-creation of the target group.
UFO_FORCE_TARGET_GROUP=1 ufo deploy demo-web --elb-eip-ids eipalloc-ac226fa4 eipalloc-b5206dbd
To remove the EIPs but still keep the network load balancer, you can specify either:
UFO_FORCE_TARGET_GROUP=1 ufo deploy demo-web --elb-eip-ids ' ' --elb-type network
UFO_FORCE_TARGET_GROUP=1 ufo deploy demo-web --elb-eip-ids 'empty' --elb-type network
Note be careful using the UFO_FORCE_TARGET_GROUP option. If the deploy fails, then the CloudFormation stack rolls back and can leave the target group with healthy targets resulting in downtime. If it’s an production service and you are changing the load balancer type or eip IPs, it is recommended to instead create a temporary additional ECS service, do a DNS switch, and then remove the old ECS.
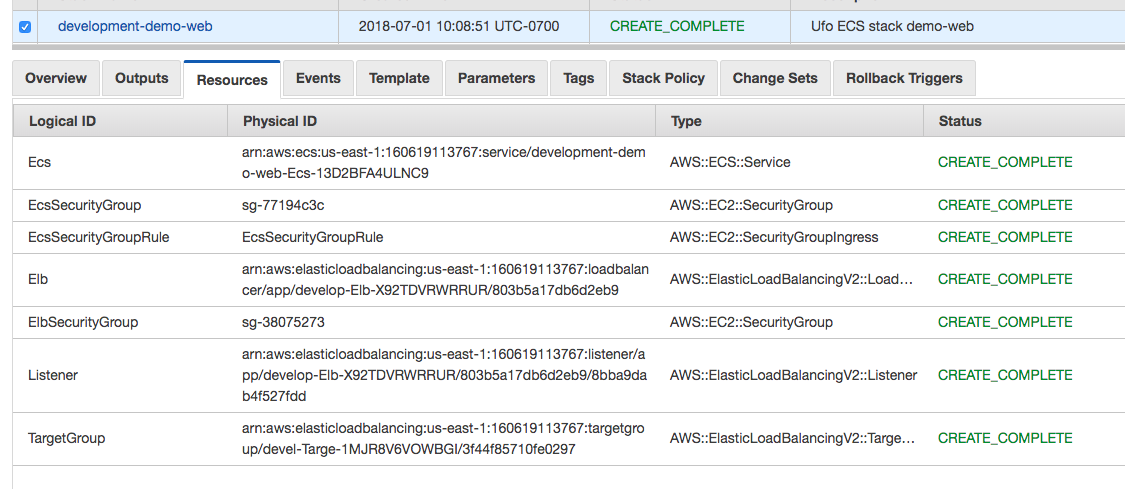
Load Balancer Implementation
Under the hood, ufo implements load balancer support with CloudFormation. You can see these resources by visiting the CloudFormation console and clicking on the corresponding stack. Here’s an example:
Pro tip: Use the <- and -> arrow keys to move back and forward.
Edit this page
See a typo or an error? You can improve this page. This website is available on GitHub and contributions are encouraged and welcomed. We love pull requests from you!
- Suggest an edit to this page (here's the contributing guide).
- Open an issue about this page to report a problem.